Ear wax, scientifically known as cerumen, serves a crucial role in protecting our ears. It acts as a natural barrier, preventing foreign particles, dust, and harmful bacteria from infiltrating the delicate ear canal. Its protective function is essential for maintaining the overall health and functionality of our ears.

Earwax becomes a problem when its natural production and expulsion mechanisms are disrupted, leading to an accumulation within the ear canal. Excessive earwax, or cerumen impaction, can cause a range of issues such as hearing loss, earaches, and tinnitus (ringing in the ears). Individuals who use hearing aids or earplugs, as well as those with anatomical variations that impede wax drainage, may be more prone to such complications.
Dark brown or black earwax results from exposure to oxygen. It may also darken due to dirt or dust in the ear canal. This wax usually requires olive oil or sodium bicarbonate use in the ear to aid removal.
A clotted or liquid red wax means there is or had been some bleeding in the ear due to an infection or damage. It is advised to seek medical attention quickly.
The discolouration of wax can occur from use of drops or external treatments for the outer ear. An oozing or smelling discharge from the ear is a sign of otitis externa or outer ear infection.
The accumulation of dead skin cells, dust, cerumen can often form along the ear canal and form a basis for ear wax build-up to occur.
It is not recommended to use objects like cotton swabs that can inadvertently push wax deeper, exacerbating the problem and potentially causing injury to the ear canal. Ear syringing with water which was previously used and offered by surgeries is no longer recommended due to the risks associated such as trauma to the eardrum and infection.
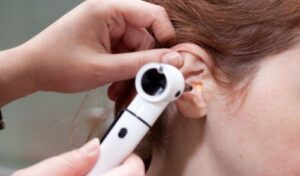
For dry and itchy ears it is recommended that you use olive oil in the ear canal (3-4 drops twice a day) for 1 – 2 weeks. In cases where the wax is impacted causing hearing loss, ringing sounds or aching it would be wise to get an ear practitioner to look inside to make an assessment on what method would be most suitable.
Microsuction is the new advanced method which vacuums the wax out of the ear provided it is not too dry or has been treated with either sodium bicarbonate drops or Olive oil.
Click here to book an appointment with an ear practitioner for microsuction or a general otoscopy – https://woodstockroadchemist.com/service/ear-wax-removal/