General queries:
info@woodstockroadchemist.comNHS prescription queries:
woodstockrd.chemist@nhs.netGeneral queries:
info@woodstockroadchemist.comNHS prescription queries:
woodstockrd.chemist@nhs.netPharmacy first scheme was launched on 31st January 2024 which enables patients to access prescription only medications such as antibiotics or antivirals if clinically deemed appropriate by the pharmacist for seven most common health conditions. This relieves some pressure off the GP surgeries while also ensuring less waiting times for the patients.
Seven common health conditions
For each of the following conditions our pharmacists can offer clinical advice and treatment options including antibiotics or antivirals.
Sinusitis (Age 12 years and over)

Sinusitis, characterized by inflammation and swelling of the sinuses, typically arises due to an underlying infection. This condition, prevalent in many individuals, often resolves spontaneously over a period of approximately four weeks. However, when symptoms persist beyond this timeframe, medical intervention becomes necessary to alleviate discomfort and facilitate recovery. Various medications, tailored to individual needs, can effectively assist in expediting the resolution of sinusitis and mitigating its lingering effects.
Sore Throat (Age 5 years and over)

A sore throat, medically referred to as pharyngitis, is a condition characterized by pain, irritation, or scratchiness in the throat. It can often be a symptom of an underlying illness such as a viral or bacterial infection, allergies, or environmental irritants like smoke or pollution. Sore throats are commonly accompanied by discomfort when swallowing, dryness, and sometimes swollen glands in the neck. While most cases of sore throat are mild and resolve on their own within a few days, severe or persistent symptoms may require medical attention to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Earache (Age 1 to 17 years)

An earache presents as discomfort or pain in one or both ears and can stem from various sources, including infections, blockages, injuries, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, or dental issues. While some cases may resolve with home remedies like warm compresses or over-the-counter pain relievers, severe or persistent earaches warrant medical attention to identify the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment, which may involve prescription medications, earwax removal, or surgical intervention if necessary.
Infected Insect bite (Age 1 year and over)

An infected insect bite occurs when harmful microorganisms enter the skin through an insect’s bite, causing inflammation and infection. Symptoms include redness, swelling, pain, and occasionally pus formation. Treatment involves cleaning the area and applying topical or oral antibiotics as necessary under medical supervision.
Impetigo (Age 1 year and over)
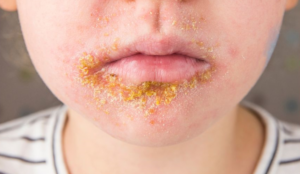
Impetigo, a bacterial skin condition, presents with red sores that swiftly burst, releasing fluid and forming a crust with a yellowish-brown hue. It is frequently triggered by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria. Primarily affecting children, this contagious ailment spreads through direct contact or by sharing personal items such as towels or clothing. Treatment usually consists of topical or oral antibiotics administered by a healthcare provider to eliminate the infection and halt its transmission. Swift intervention is crucial to avert complications and expedite recovery.
Shingles (Age 18 years and over)
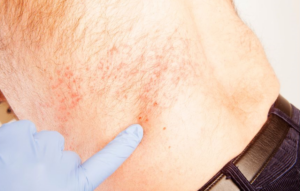
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox. It typically presents as a painful rash or blisters along a specific nerve pathway. Reactivation of the virus, often triggered by factors like aging or stress, leads to symptoms such as itching, burning, and fluid filled blisters. While antiviral medications can help manage symptoms and shorten the duration of the outbreak, vaccines are available for prevention or reducing the severity of shingles. Early treatment is crucial to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications.
Uncomplicated urinary tract infections in women (Age 16 to 64)

Uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) in women denote bacterial infections primarily affecting the lower urinary tract, such as the bladder and urethra, without complicating factors involving the kidneys or other complexities. These infections typically arise from bacterial colonization, with Escherichia coli being the most common culprit. Symptoms often include frequent urination, a burning sensation when urinating, urgency, and discomfort in the lower abdomen. While uncomplicated UTIs generally lack underlying health conditions, timely treatment with antibiotics is crucial to prevent kidney involvement or other potential complications. Adequate fluid intake and adherence to good hygiene practices also play pivotal roles in managing and preventing uncomplicated UTIs in women.